- Show Menu
- Contact Us
- FAQs
- Reader Service
- Survey Data
- Survey Winners
- Testimonials
- Upcoming Events
- Webinars
- White Papers
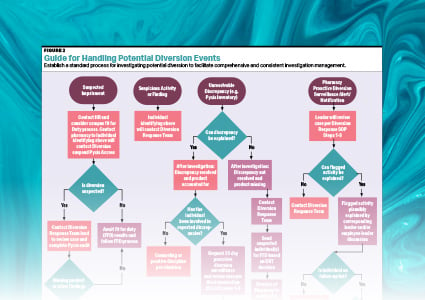
Engineering Controls—BSCs/RABS
Engineering controls serve as the backbone of the compounding operation. Just as every compounding operation is unique, there is no standard approach to the utilization of engineering controls. While LAFWs are widely used and Type II A2 BSCs are quite common, an array of additional equipment options serve to support effective cleanroom operations.
Note that the terms Compounding Aseptic Isolators (CAIs) and Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolators (CACIs) have been replaced with the term Restricted Access Barrier Systems (RABS) as it is a more apt description of this technology and also avoids any confusion with the similarly named, but very different pharmaceutical isolators. These isolators are typically used in pharmaceutical manufacturing and feature a built-in, automated decontamination system. A few hospital pharmacies have adopted this advanced technology in their cleanrooms and we will watch to see if this trend continues.

LAFWs and BSCs are widely used in hospital pharmacies and one-third of all facilities also take advantage of RABS to support compounding safety.

Most facilities rely on Class II, Type A2 BSCs for their compounding needs.

Nuaire continues to lead the RABS marketplace, followed by Germfree, The Baker Company, and Isotech Design.

In many facilities, pharmacy continues to utilize RABS in segregated compounding areas rather than in cleanrooms.

Facilities of all sizes are considering adding additional RABS to their compounding complex.

Pharmaceutical isolators, the advanced technology typically used in pharmaceutical manufacturing that features a built-in automated decontamination system, are rarely found in pharmacy. Just 4% of facilities currently utilize this technology, while another 4% are planning to purchase it in within the next 5 years.
Like what you've read? Please log in or create a free account to enjoy more of what www.pppmag.com has to offer.